- About us
- Departments
- Emergency Medicine
- Anaesthesiology & Critical Care
- Gastroenterology & Liver Transplant
- Dental & Cosmetic Surgery
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
- Internal Medicine
- Diabetology
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- Pulmunology
- Paediatrics & Neonatology
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Urology & Andrology
- Endocrine Surgery
- Services
- Robotic Surgery
- Contact us
- Select Your Language
Navigating the Stages of Cervical Cancer: From Prevention to Treatment
Introduction
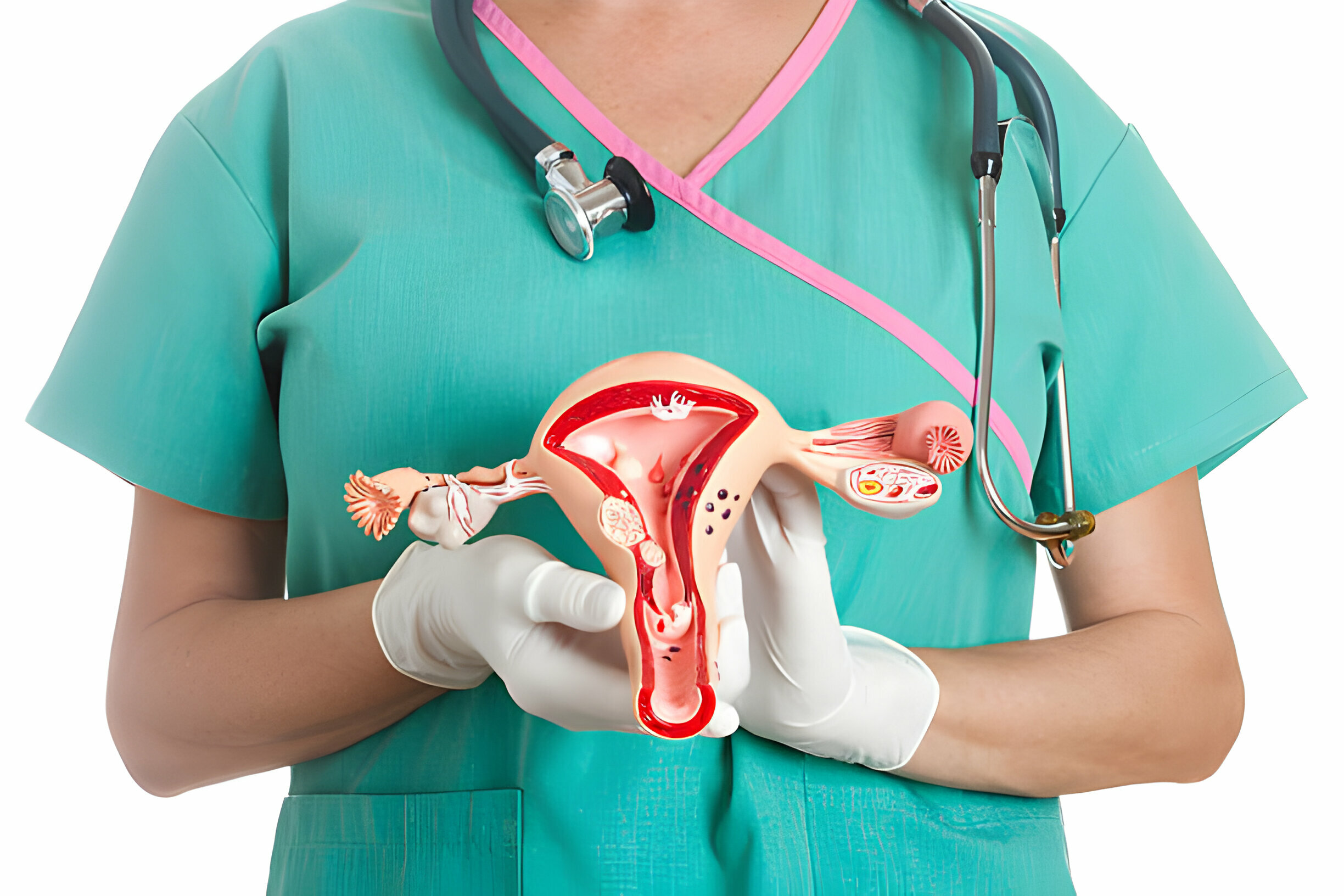
Cervical cancer is a significant concern for women’s health worldwide, and understanding its stages, risk factors, and preventive measures is crucial. This blog will delve into the various aspects of cervical cancer, including HPV (Human Papillomavirus), Pap smear screening, stages of cervical cancer, treatment options, and the role of gynecological oncology in managing this condition.
Understanding Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer typically starts with the presence of HPV, a sexually transmitted infection. HPV infection can lead to changes in the cells of the cervix, which may eventually progress to cervical cancer if left untreated. Regular cervical screenings, such as Pap smears, play a pivotal role in early detection, as they can identify abnormal cell changes in the cervix.
Cervical Screening and Prevention
Cervical screening, often referred to as a Pap smear, is a critical tool for the early detection of cervical cancer. During a Pap smear, a healthcare provider collects cells from the cervix, which are then examined for abnormalities. Early detection through regular screenings can help prevent the progression of cervical cancer by enabling prompt intervention.
Preventive care goes beyond Pap smears. The HPV vaccine, available to both girls and boys, offers protection against the most common HPV strains that cause cervical cancer. Vaccination is an essential part of cervical cancer prevention, along with safe sexual practices and regular check-ups with a gynecologist.
Stages of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is typically classified into several stages, each representing the extent of the disease’s progression. These stages are crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment plan:
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ): At this stage, cancerous cells are confined to the surface of the cervix, making it highly treatable with a good prognosis.
Stage I: In this stage, cancer is limited to the cervix itself. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination of both.
Stage II: Cancer has spread beyond the cervix to nearby tissues. Treatment often involves surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to the lower part of the vagina or the pelvic wall. Treatment becomes more aggressive, combining radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Stage IV: Cancer has metastasized to distant organs, such as the lungs or liver. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
Surgery: Surgery may involve removing the tumor or the entire cervix (hysterectomy) and nearby lymph nodes.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be external or internal (brachytherapy).
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs are administered to kill cancer cells throughout the body, especially in advanced stages.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies aim to inhibit specific molecules involved in cancer growth and spread. They are often used in combination with other treatments.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy enhances the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
The Role of Gynecological Oncology
Gynecological oncologists are specialists who focus on the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological cancers, including cervical cancer. They possess expertise in the latest treatment modalities and play a vital role in managing cervical cancer cases. Patients with cervical cancer are often referred to gynecological oncologists for personalized care and treatment planning.
Cervical cancer is a significant health concern, but with proper preventive care, early detection through Pap smears, and timely treatment, its impact can be minimized. Understanding the stages of cervical cancer, risk factors like HPV, and the role of gynecological oncology can empower women to take charge of their health and reduce the risk of this disease. Regular check-ups, vaccination, and informed decisions are key elements in the battle against cervical cancer, promoting better women’s health worldwide.